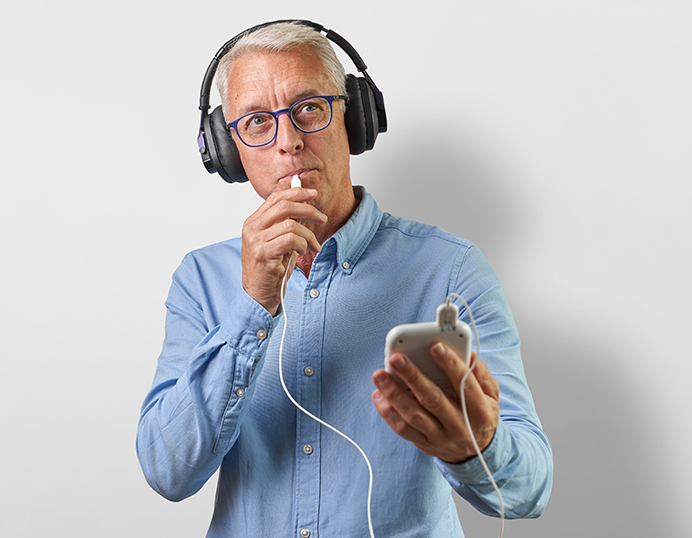
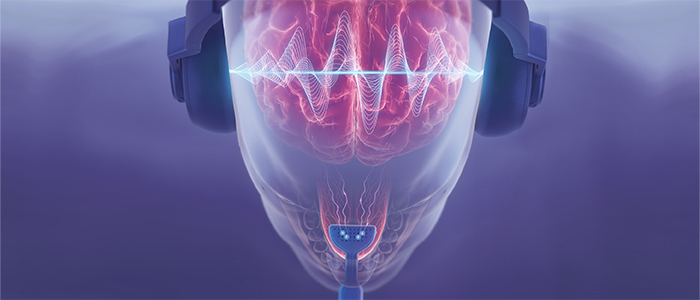
How Lenire Treats Tinnitus
83% of Patients Recommend Lenire 4

Life Changing Solution
Tinnitus can be distressing and cause sleep, social and concentration issues. Lenire soothes tinnitus so you can live life your way.

Safe and Effective
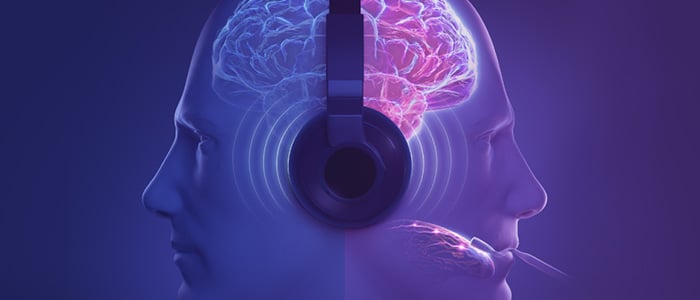
Lenire’s dual mode stimulation has been proven safe and more effective than sound-only therapy for moderate or worse tinnitus. 3

Trusted by Specialists
Lenire works with hearing care and tinnitus experts worldwide to ensure patients receive the best quality of care.
What is Lenire?
Lenire is first and only dual mode technology for the treatment of tinnitus granted US FDA approval. Large scale clinical trial results show the device to be a safe and effective tinnitus treatment. 4
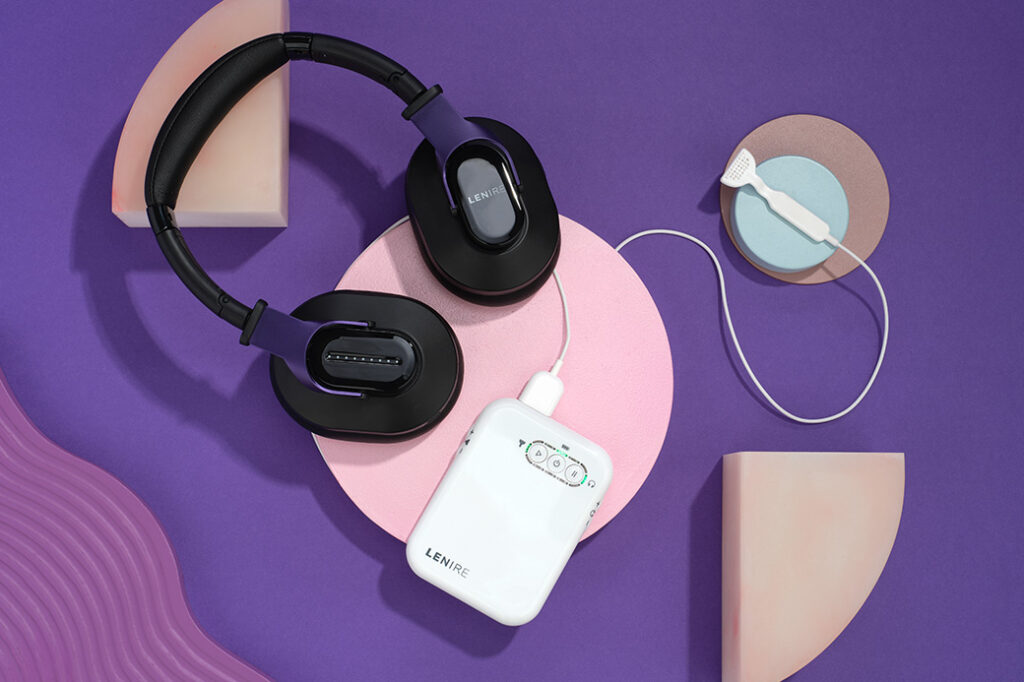

Patient Success Stories
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus affects up to 15% of people and can be experienced as a ringing or buzzing in the ears. A person with tinnitus hears noise when there is no external source.

Proven in Three Large Clinical Trials
FDA Approved. Independently Verified. Real World Validated.

First Clinical Trial
80% of Lenire’s first clinical trial patients had a reduction in tinnitus severity that sustained for at least 12 months after treatment. 1
Second Clinical Trial
91% of Lenire’s second clinical trial patients had a reduction in tinnitus severity that sustained for at least 12 months after treatment. 2
Third Clinical Trial
Majority of patients with moderate or worse tinnitus had significant relief using Lenire when sound-only had no meaningful impact.3
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is tinnitus?
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when there is no external source. Tinnitus is a very common condition that affects 10 – 15% of people. At present, there is no cure for tinnitus. However, Lenire has been proven to significantly reduce tinnitus severity.
-
What are the types of tinnitus?
Watch Neuromod Clinical Training Manager, Dr. Sarah Matthews discuss Different Types of Tinnitus on Talking Tinnitus.
Generally speaking, there are two types of tinnitus: Subjective Tinnitus and Objective Tinnitus.
- Subjective Tinnitus is tinnitus that only the person themselves can hear. This is the most common type of tinnitus.
- Objective Tinnitus is tinnitus that your doctor can hear during an examination. This rare type of tinnitus may be caused by a blood vessel problem or ear muscle contractions.
Lenire is a bimodal neuromodulation device that treats Subjective Tinnitus. As well as the two many types of tinnitus, there are also subtypes – Somatic Tinnitus, Cochlear Tinnitus, and Central Tinnitus.
- Somatic or Somatosensory Tinnitus is when tinnitus changes in pitch, volume, location, or the type of sound you hear when you move your head, neck, jaw, or face. TMJ and other dental issues such as bruxism or malocclusion, cervical, spinal, and head injuries, and even muscle tightness are all causes of somatic tinnitus. Somatic tinnitus is present in 65 to 80% of people with tinnitus.
- Cochlear Tinnitus occurs when something affects the health of the ear resulting in abnormal neural activity in the cochlea, resulting in the perception of tinnitus. Hearing loss, noise exposure, ototoxic medications, ear diseases, and medical conditions such as diabetes and cardiac conditions are all common causes of cochlear tinnitus.
- Central Tinnitus is when abnormal patterns of spontaneous activity in the auditory brain center result in tinnitus. The activity typically begins when tinnitus has become a chronic condition. Once this occurs, the brain starts to react to the presence of somatic and cochlear tinnitus. We can see these changes start to occur as soon as 12 weeks (about 3 months) after the start of tinnitus.
If you are experiencing tinnitus, it is recommended to seek advice from a medical professional with an understanding of tinnitus. You can find a tinnitus specialist near you by visiting www.lenire.com/find-a-clinic/.
-
What do I do if I have tinnitus?
Watch Peachetree Hearing Owner, Dr. Melissa Wikoff discuss when you should seek help for tinnitus on Talking Tinnitus.
Identifying the specific cause of tinnitus can be challenging.
Resolving tinnitus causes such as an ear infection, or a build up of earwax may provide relief from tinnitus. However, as there are many causes of tinnitus, it is recommended that people who notice tinnitus should speak with an audiologist that specialises in tinnitus care.
A tinnitus specialist can conduct a tinnitus assessment to diagnose the underlying cause of tinnitus. They can also explain management techniques or treatment options, such as Lenire.
You can find an audiologist that specializes in tinnitus care by visiting www.lenire.com/find-a-clinic/.
-
What are the causes of tinnitus?
Hearing loss, as a result of ageing, is the most common cause of tinnitus.
Other common causes include eardrum perforation, middle ear infection, Ménière’s Disease, sudden exposure to loud noise, certain medications, head injury, temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) and stress.
Less commonly, tinnitus is linked to hearing loss caused by a blockage or ear condition that affects the outer or middle ear and stops sound waves from passing into the inner ear.
-
Is there a cure for tinnitus?
Watch New York Hearing Doctors’ Dr. Craig Kasper answer “Is Tinnitus Treatable?” on Talking Tinnitus.
No but tinnitus is treatable. Lenire is clinically proven to provide relief from tinnitus. Lenire’s clinical trials have demonstrated that the medical device is effective at soothing tinnitus. Additionally, Lenire has been proven to be more effective than audio-only therapy at soothing tinnitus.
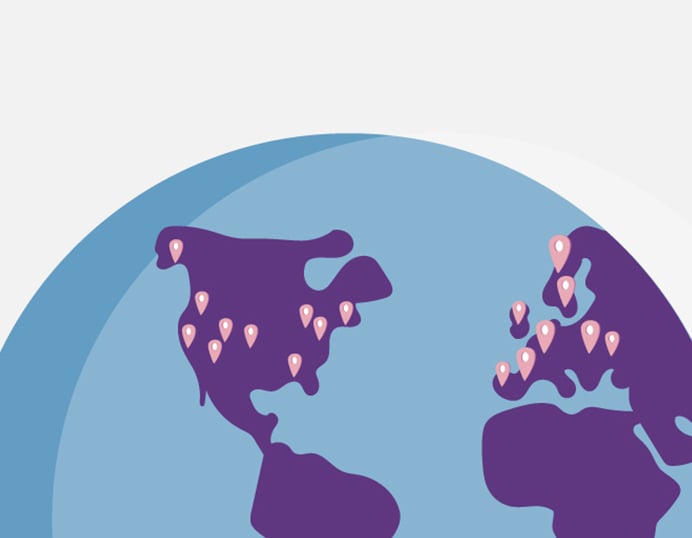
Find a Clinic
Neuromod Devices has expert Partner Clinics across America, Europe, and the United Kingdom. Use the Find a Clinic Map to start your treatment with Lenire.
Resources and Success Stories
Learn how it works and how our three large-scale clinical trials were designed.
Watch this video to hear how trained audiologists treat tinnitus patients with Lenire.
Learn how you can manage tinnitus and find more resources on the blog.
1. TENT-A1 Conlon et al., Sci. Transl. Med. 12, eabb2830 (2020)
2. TENT-A2: Conlon et al., Different bimodal neuromodulation settings reduce tinnitus symptoms in a large randomized trial, Sci Rep.
3. TENT-A3: Clinical trial data in preparation for independent publication: clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05227365.
4. Aggregate: TENT-A1, TENT-A2, TENT-A3 aggregate clinical trial results.
Note 1: All statistics based on compliant patients. Patient compliance criteria is detailed in Lenire’s clinical trial design.
Note 2: TENT-A1/TENT-A2 were not considered by the United States of America FDA as part of Lenire’s FDA Grant and, as such, applies solely to outside the US.
